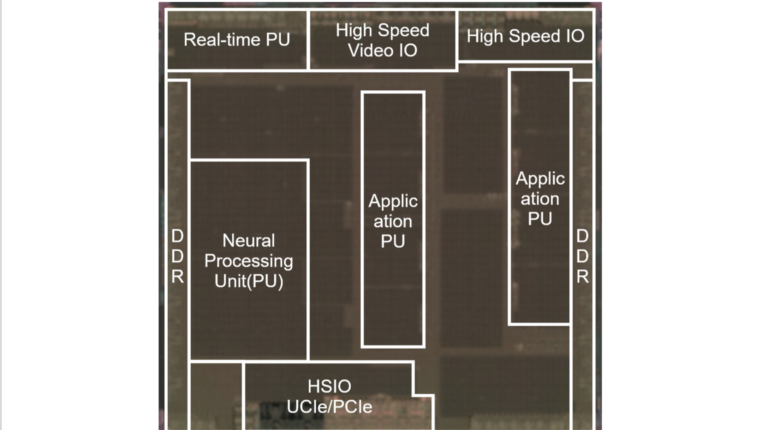
Renesas Electronics has developed three system-on-chip (SoC) technologies for automotive multi-domain electronic control units. They feature advanced AI processing capabilities and chiplet functions, serving as the core technology platform for next-generation automotive electrical/electronic (E/E) architectures.
In the era of software-defined vehicles, automotive SoCs must deliver high performance to support multiple simultaneous applications and provide scalability through chiplet architectures, and must also comply with automotive functional safety standards. As multi-domain SoCs for centralized computing increase in size and complexity, maintaining automotive-grade quality becomes more challenging. Higher performance also drives greater power consumption, making power efficiency and safety improvements essential. To address these requirements, Renesas Electronics has developed new technologies.
Chiplet architecture
To meet the functional safety requirements of automotive SoCs, Renesas has developed a proprietary architecture that supports ASIL D even in a chiplet configuration. By combining the standard die-to-die UCIe interface with a proprietary RegionID mechanism, the architecture prevents interference with hardware resources, even when numerous applications run simultaneously, thereby achieving freedom from interference (FFI).
Conventional UCIe interfaces lack functionality to transmit RegionIDs between dies. Renesas developed a method for mapping RegionIDs into physical address space, encoding them into the UCIe region and transmitting them. This enables safe access control through the memory management unit and real-time cores, and meets functional safety requirements across chiplets. Additionally, by maintaining bandwidth from processors to the memory bus, the UCIe interface was confirmed through testing to achieve a high transmission speed of 51.2GB/s, approaching the upper limit of intra-SoC transfer speeds. This technology provides both scalability and safety for high-performance automotive SoCs.
AI processing capabilities and automotive-grade quality
Automotive-grade quality is essential for SDV systems. Renesas Electronics has developed a 3nm SoC design that enhances neural processing unit (NPU) performance for AI workloads while maintaining automotive-grade quality.
In recent years, NPUs have increased in size, growing larger by approximately 1.5 times compared to previous generations. This expansion has increased clock latency between shared clock sources and individual circuits. To address this, Renesas redesigned the clock architecture by dividing clock pulse generators (CPGs), previously implemented at the module level, and introducing mini-CPGs (mCPGs) at the sub-module level. This approach reduces clock latency and satisfies timing requirements.
However, multi-layer mCPGs complicate test clock synchronization, which is critical for achieving zero defects in automotive applications. Renesas has integrated test circuits into the hierarchical CPG architecture and unified the signal path for user clocks and test clocks. The design also synchronizes upper- and lower-level mCPGs under a single clock source in test mode.
Advanced power control and monitoring
To meet the performance, power efficiency and safety requirements of advanced automotive SoCs, Renesas Electronics has developed an advanced power-gating architecture with more than 90 power domains. This enables fine-grained power control, ranging from several milliwatts to several tens of watts, depending on operating conditions.
To address IR drops (voltage drops) caused by higher current density in smaller process nodes, Renesas divided power switches (PSWs) into two types: ring PSWs and row PSWs. When power is applied, the ring PSW limits rush currents. The row PSW then balances impedance within the domain. Together, these measures reduce IR drops by approximately 13% compared with conventional designs.
To comply with ASIL D functional safety requirements, Renesas Electronics uses a dual core lockstep (DCLS) architecture in which the master and checker cores are controlled by independent power switches and controllers. This configuration enables fault detection through lockstep comparison, even if one side fails.
In addition, loopback monitoring is applied to each power switch (PSW) gate signal, enabling detection of unintended OFF states. Voltage monitoring is performed using a digital voltage monitor (DVMON) designed to resist temperature drift, improving aging tolerance by 1.4mV. Together, these technologies support high-performance automotive SoCs with enhanced power efficiency and functional safety.
These new technologies are being used in Renesas’s R-Car X5H SoC for automotive multi-domain ECUs. With R-Car X5H, users can accelerate the evolution of SDVs while ensuring safety and enabling autonomous driving, digital cockpit and more.
Related news, Mahindra selects Mobileye ADAS for six future models